Unpacking Iran's Religious Identity: Is Iran Sunni Or Shia?
Many people wonder about the religious makeup of Iran, a country that often appears in world news. It's a fair question, really, considering how much religion shapes daily life and national actions in many places. Knowing the main religious branch in Iran can help make sense of its history, its culture, and even its place in the world today. It's a rather important piece of information, you know, for anyone wanting to get a clearer picture of this ancient land.
This land, which has been a cradle of civilization for thousands of years, was home to many different groups long before its current form came to be. It's a country with a very rich and special way of life, something that has continued for a very long time, actually. You see, Iran is a mountainous place, quite dry, and it has many different kinds of people living there, especially in southwestern Asia, so it's quite diverse.
So, when we talk about Iran, we are looking at a nation with a deep past and a present that draws a lot of attention, from its capital, Tehran, being a big financial hub to its ongoing discussions on the world stage. To really get a feel for what makes this country what it is, we need to look closely at its main religious identity. It's a question that comes up quite a bit, and for good reason, I mean, it tells you a lot.
Table of Contents
- The Straight Answer: Iran's Shia Majority
- A Look Back: How Iran Became Shia
- The Sunni Presence in Iran
- How Religion Shapes the Islamic Republic
- Iran's Diverse Face: Beyond Religion
- Common Questions About Iran's Religious Identity
The Straight Answer: Iran's Shia Majority
When you ask if Iran is Sunni or Shia, the clear answer is that it's overwhelmingly Shia. To be honest, this makes Iran quite unique in the wider Muslim world, where Sunni Islam is the most common form. In Iran, a very large portion of the people, perhaps around 90% or even more, follow Shia Islam, specifically the Twelver branch, which is the official state religion. So, it's pretty much a Shia nation.
This strong Shia identity is something that sets Iran apart, especially from many of its neighbors in the Middle East. It's a key part of the country's national character and has been for centuries. You see this influence everywhere, from public holidays to the structure of the government itself. It's really quite central to everything, in a way.
The "Islamic Republic" title, which is what Iran calls itself, truly reflects this deep connection to its Shia faith. It's not just a name; it shows how the country's laws and how it runs things are very much tied to religious principles. This is a big part of what you'll find when you look at the news from Iran, which often covers its politics, its economy, and its foreign policy, all seen through this particular lens, you know.
A Look Back: How Iran Became Shia
The story of how Iran became a Shia-majority nation is a long one, stretching back many hundreds of years. For a long time after the first spread of Islam, Iran, like many other places, had a mix of religious views, with Sunni Islam being quite common. It wasn't always the Shia stronghold it is today, which is kind of interesting to think about, actually.
The Safavid Turning Point
The big shift happened with the rise of the Safavid dynasty in the early 16th century. Before them, Iran was mostly Sunni. But the Safavid rulers, especially Shah Ismail I, made Shia Islam the official religion of their empire. This was a really big change, a bit of a turning point for the whole region, you could say.
They worked very hard to spread Shia teachings throughout the land, sometimes even forcing people to change their beliefs. They brought in Shia scholars from other places and put in place religious schools and institutions to support the new official faith. This effort was quite thorough, and over time, it deeply changed the religious landscape of the country. It was, you know, a very deliberate process.
This historical move by the Safavids created a distinct Iranian identity that was different from the mostly Sunni Ottoman Empire next door. This religious difference has shaped relations between Iran and its neighbors for centuries, and it still plays a part in regional tensions even today, as a matter of fact. It's a long shadow from history, you might say.
Shia Islam: A Brief Explanation
To really get why this matters, it helps to know a little about what makes Shia Islam different from Sunni Islam. The main difference goes back to who should have led the Muslim community after the passing of Prophet Muhammad. Sunnis believe that the leader should be chosen by the community, while Shias believe the leadership should have stayed within the Prophet's family, specifically through his son-in-law, Ali ibn Abi Talib, and his descendants, known as Imams. So, it's about leadership, basically.
For Shias, these Imams are seen as very special spiritual guides who have a deep understanding of God's message. The Twelver Shia, who are the majority in Iran, believe in twelve such Imams, with the last one, the Mahdi, believed to be in hiding and expected to return. This belief in the Imams, and the idea of religious scholars acting as their representatives in their absence, is a very central part of Shia faith. It really is, you know, a core belief.
This focus on the Imams and their lineage gives Shia Islam a unique structure and way of looking at religious authority. It means that religious leaders, often called ayatollahs, have a very important place in society and politics, especially in a country like Iran, where Shia Islam is the official faith. This is why you hear about religious figures having a lot of say in the country's direction, which is pretty much the case.
The Sunni Presence in Iran
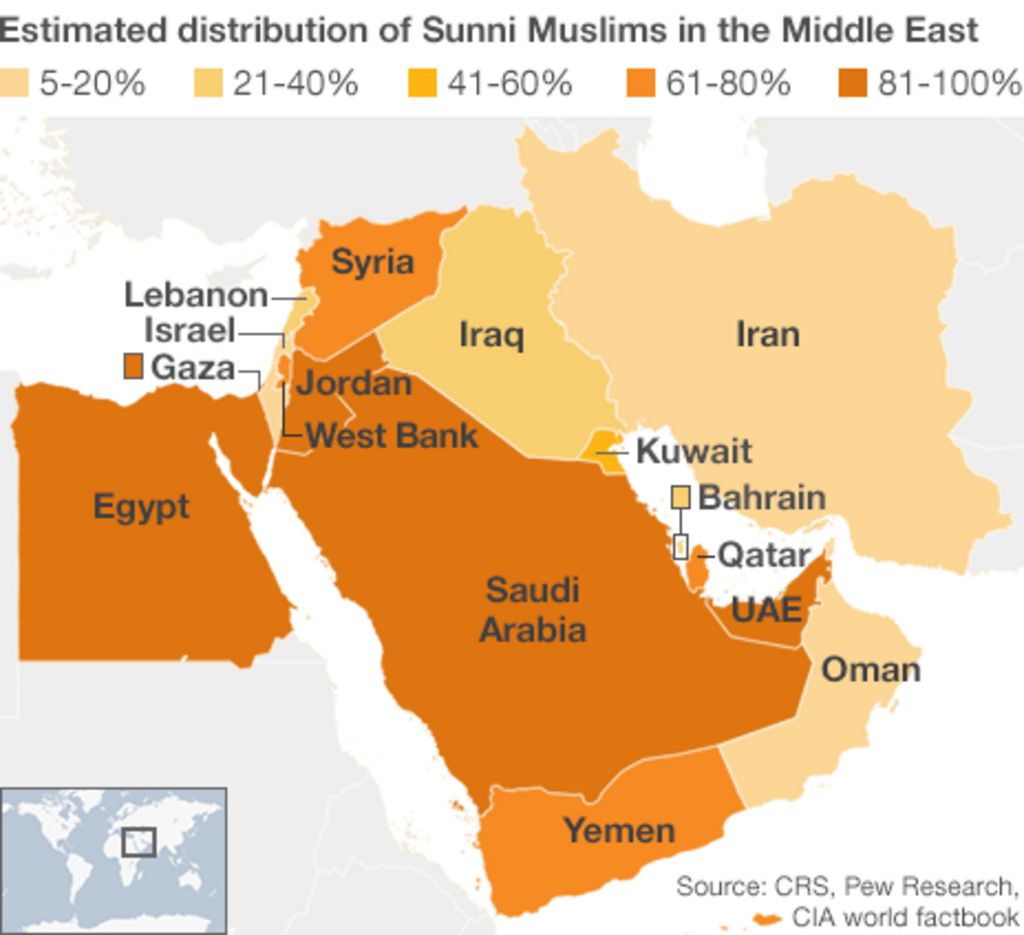
Even though Iran is mostly Shia, it's worth remembering that there are Sunnis living there too. They form a smaller group, but they are a real part of the country's diverse population. These Sunni communities are often found in certain parts of the country, especially in areas near the borders with other countries that have large Sunni populations. So, they are there, you know.
For example, you'll find Sunni communities in regions like Kurdistan, Sistan and Baluchestan, and parts of the Persian Gulf coast. These groups often have their own unique ethnic backgrounds, like Kurds, Baluchis, and Arabs, and their Sunni faith is a big part of their identity. Iran, after all, is an ethnically diverse country, as a matter of fact, with many different peoples.
While Shia Islam is the state religion and has a dominant role, these Sunni groups maintain their own religious practices and traditions. Their presence adds another layer to the country's rich social fabric, showing that even in a place with a clear majority faith, there's still a lot of variety. It's kind of interesting to see that mix, you know.
How Religion Shapes the Islamic Republic
The fact that Iran is an Islamic Republic, with Shia Islam as its main religion, truly shapes almost every part of its national life. This isn't just about what people believe in their hearts; it affects how the country is run, how it deals with other nations, and even the daily lives of its people. It's a pretty big deal, actually.
Politics and Foreign Relations
The country's political system, for instance, is built around religious principles, with top religious leaders having a very strong say in how things go. This means that religious laws and interpretations guide many decisions, from national policies to international agreements. You can see this in the news when you hear about Iran's foreign policy or its nuclear talks; religious views often play a part, so they do.
This religious identity also plays a big role in Iran's relations with other countries, especially those in the Middle East. Its support for Shia groups in other nations and its differences with mostly Sunni countries often create regional tensions. The idea of the "Islamic Republic" is not just a name; it’s a guide for its actions on the world stage, which is pretty much the case.
For example, Iran's position on certain international issues, like its stance on the Israeli-Palestinian conflict or its interactions with European diplomats, is often seen through the lens of its Shia ideology. It's a very clear part of its approach to global affairs, you know, influencing many of its diplomatic efforts.
Cultural and Social Life
Beyond politics, Shia Islam deeply affects Iran's cultural and social life. Religious holidays, ceremonies, and traditions are a very important part of the year. The mourning month of Muharram, for example, is a very significant time for Shias, and it's observed with great feeling across the country. It's a truly central part of their shared experience.
The education system, the media, and even everyday social norms are all influenced by Shia teachings. This helps to maintain the country's rich and very special way of life, something that has continued for a very long time, as a matter of fact. It's a continuity that goes back centuries, shaping what it means to be Iranian.
Even things like the architecture, the arts, and the way people dress can show the influence of this dominant religious identity. It's woven into the very fabric of society, creating a distinct cultural environment that is quite different from many other places. It's a very unique blend, really.
Iran's Diverse Face: Beyond Religion
While the religious identity of Iran is very strong, it's also important to remember that the country is much more than just its dominant faith. Iran is a place of amazing geographical variety, from its mountains to its arid plains, and it sits between the Caspian Sea in the north and the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman in the south. This geographical position has always made it a crossroads of cultures, you know.
Tehran, the nation's capital, is a very large city and a major financial center, a place where modern life and ancient traditions meet. It's a bustling hub of activity, where you can see the many sides of Iran's present, even as it deals with challenges like a severe water crisis, which is a bit of a concern for the city, actually.
The country's history as a cradle of civilization means it has been home to many different groups and ways of life for thousands of years. This long history contributes to its ethnic diversity, with various peoples living alongside each other, each adding to the country's unique character. You can learn more about Iran's diverse regions on our site, which really shows how varied the country is.
So, while the question "Is Iran Sunni or Shia?" has a clear answer, it's just one piece of a much larger and more interesting picture. Understanding this religious aspect helps us appreciate the depth of Iran's identity, but it's just a starting point for exploring this truly fascinating country. You can also read more about Iran's history and geography to get a fuller picture, if you like.
Common Questions About Iran's Religious Identity
What makes Shia and Sunni Islam different?
The main difference between Shia and Sunni Islam goes back to a disagreement about who should have led the Muslim community right after the passing of Prophet Muhammad. Sunnis believe that the leader, or caliph, should be chosen by the community, while Shias believe that leadership should have stayed within the Prophet's family, through his son-in-law Ali and his descendants, known as Imams. So, it's really about the line of leadership, basically.
Shia Muslims, especially the Twelver Shia who are common in Iran, believe in a series of twelve divinely appointed Imams, who are seen as very special spiritual guides. Sunnis, on the other hand, do not believe in these Imams in the same way. This difference in how they see religious authority and leadership is quite fundamental, you know, and it shapes many other aspects of their faith.
These differing views also lead to some variations in religious practices, laws, and interpretations of Islamic texts. While both branches share the core beliefs of Islam, like the belief in one God and the Prophet Muhammad, these historical and leadership differences are very important to their distinct identities. It's quite a significant split, you see.
Are there many Sunnis living in Iran?
While Iran is largely a Shia country, there are certainly Sunnis living there, but they form a minority group. Their numbers are much smaller compared to the Shia majority, perhaps around 5-10% of the population. These Sunni communities are often found in specific parts of the country, especially in border regions, as a matter of fact.
For instance, you'll find significant Sunni populations in provinces like Kurdistan in the west, which borders Iraq, and Sistan and Baluchestan in the southeast, which borders Pakistan and Afghanistan. These communities often belong to different ethnic groups, such as Kurds, Baluchis, and some Arabs, who have historically followed Sunni Islam. So, they are quite concentrated in certain areas, you know.
Despite being a minority, these Sunni groups have their own mosques and religious schools, and they maintain their distinct cultural and religious practices. Their presence adds to the rich mix of cultures and peoples that make up Iran, showing the country's wider diversity beyond its main religious identity. It's a pretty interesting aspect of the country, really.
What does "Islamic Republic" mean for Iran?
The term "Islamic Republic" means that Iran's government and its laws are based on Islamic principles, specifically those of Shia Islam. After the 1979 revolution, Iran changed from a monarchy to this new system, where religious scholars and leaders play a very central role in how the country is run. It's a system where religious law, or Sharia, is the main source of all laws, which is pretty much the case.
This means that the country's constitution, its legal system, and many of its political institutions are designed to reflect and uphold Islamic values and teachings. For example, the Supreme Leader, who is a top religious authority, has the final say on major state policies. This structure is very different from a secular republic, where religion and government are kept separate, you know.
The "Islamic Republic" title also means that the country's foreign policy and its social rules are often guided by religious considerations. This impacts everything from human rights policies to international relations, making religion a very important factor in how Iran interacts with the world and how its people live their daily lives. It's a very defining feature, actually.

Behind Stark Political Divisions, a More Complex Map of Sunnis and
Sunnis and Shia in the Middle East - BBC News

Sunnis and Shia: Islam's ancient schism - BBC News