Who Is Making Government In India? A Look At How It All Comes Together
Have you ever stopped to think about who is making government in India, and how that whole process actually works? It's a pretty big deal, you know, figuring out how a country as vast and diverse as India gets its leaders and its laws. Really, it’s about the act or process of forming, causing, doing, or coming into being, which is what "making" means in this context. We're talking about the creation, the production, the very assembly of the system that guides the nation, and that, in a way, touches everyone's lives.
This process of making a government is more than just a simple vote; it's a complex, multi-layered operation. It involves a lot of different parts, like the people themselves, the rules set down in the constitution, and the various bodies that work together. So, it's not just one person or one group, but rather a collective effort, a kind of grand collaboration that shapes the country's direction.
Understanding this system can feel a bit like looking at a really intricate machine, but it’s actually quite fascinating once you get a handle on the main parts. From the local neighborhoods all the way up to the national stage, there are specific steps and roles that define how India's government gets put together, and that’s what we'll explore today, to be honest.
Table of Contents
- How India Makes Its Government
- The Foundational Pieces of Indian Governance
- The Three Layers of Law-Making
- The Federal Structure: A Shared Responsibility
- Forming the Union Government: The Lok Sabha Elections
- The Role of Coalition Governments
- Accountability in the Process
- What the Government Does Once It Is Made
- Frequently Asked Questions About Government Formation
- Shaping the Future Together
How India Makes Its Government
When we talk about "making" the government in India, we're really talking about the act of forming it, or causing it to come into being, you know. It's the whole process of growth or development, much like how a child grows up, or how a project comes to life. This process involves using skills, knowledge, and resources to create something, taking raw ideas and turning them into a functioning system. It's a rather involved procedure, honestly, that brings together different parts of the country.
The system India uses to choose its government is based on a set of rules and practices that have evolved over time. It's not a single event, but a series of interconnected actions that lead to the formation of governing bodies at different levels. This ensures that various voices from across the nation can be heard and represented, which is pretty important for a country of India's size.
So, the "making" here isn't just about electing someone; it's about the entire framework that allows for those elections, the rules for who can govern, and how they operate once they are in power. It's a continuous activity, a process of producing something vital for the country's well-being. This whole operation, in a way, keeps the wheels of the nation turning, you see.
The Foundational Pieces of Indian Governance
The very foundation of how government is made in India rests on its Constitution. This incredibly important document, a rather detailed analysis of its making shows, involved a lot of work and careful formulation. It wasn't something that just appeared; it was a creation, a production, a kind of complex composition that took considerable effort. The Constitution outlines the sources of power, the various committees that helped shape it, and all the debates that went into its making, which is quite fascinating, really.
This foundational text defines the basic structure and principles upon which the entire governmental system is built. It sets the stage for how leaders are chosen, what their powers are, and how they are held accountable. Without this crucial document, the process of "making" a government would be, well, a bit chaotic, you might say. It provides the essential material or qualities needed for the development of the entire political system.
The Constitution, therefore, is like the blueprint for the entire government-making process. It's what allows for the orderly selection of representatives and the establishment of rules for governance. It's a living document, too, in some respects, guiding the nation's political journey and ensuring a stable framework for the creation and operation of its leadership.
The Three Layers of Law-Making
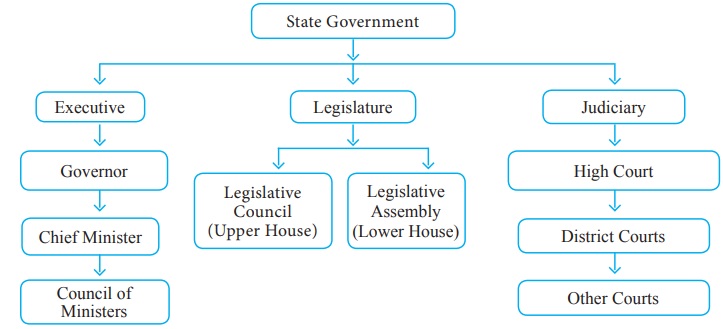
In India, the process of making laws and, by extension, forming government, happens across mainly three legislative bodies. This layered approach helps manage the vastness and diversity of the country, ensuring that governance is relevant at different scales. It's a system that, quite simply, distributes power and responsibility, which is rather clever.
Local Self-Government: The Grassroots Level
At the very foundation of this structure is the local self-government. This includes bodies like a Gram Panchayat in rural areas or a Municipality or Corporation in urban centers. These are the closest to the people, dealing with everyday issues that affect communities directly. They are, in a way, the first step in the "making" of governance, addressing immediate needs.
These local bodies are crucial because they allow for direct participation and decision-making at the community level. They handle things like local infrastructure, sanitation, and basic services. Their formation, through local elections, is a fundamental part of how governance is made accessible and responsive to the specific needs of different areas. It's a very hands-on kind of making, you know.
The importance of these local governments cannot be overstated. They are where many people first experience the democratic process and where the initial steps of collective decision-making take place. They are, essentially, the building blocks for the larger governmental structure, and that's pretty significant.
State Legislative Assemblies: Regional Voices
Above the local self-governments, you find the state legislative assembly. Each state in India has its own assembly, which is responsible for making laws specific to that state. These assemblies are formed through state-level elections, where people vote for representatives who will then form the state government. This is a vital layer in the overall process of who is making government in India, as it reflects regional priorities.
The state assemblies have a wide range of powers, covering areas like public order, agriculture, and health within their respective states. The political parties that win a majority of seats in these elections form the state government, with their leader typically becoming the Chief Minister. This process is, in some respects, a miniature version of how the national government is formed, but with a focus on state-specific matters.
These state governments play a huge role in the daily lives of citizens, implementing policies and managing resources at a regional level. Their formation is a clear example of the "making" process in action, bringing together elected representatives to serve the needs of their state. It's a rather direct link between the voters and the policies that affect them, you might say.
The Parliament of India: The National Voice
At the very apex of India's legislative structure is the Parliament of India. This is the supreme legislative body of the government of the Republic of India. It's a bicameral legislature, meaning it has two houses: the Rajya Sabha, which is the Council of States, and the Lok Sabha, which is the House of the People. This is where the big national decisions get made, you know.
The Lok Sabha, in particular, is central to forming the national government. Members of the Lok Sabha are directly elected by the people through general elections. The political party or coalition of parties that wins a majority of seats in the Lok Sabha forms the Union Government, often called the Central Government. The leader of this majority group typically becomes the Prime Minister, which is a rather significant role.
The Parliament's role in "making" the government is absolutely critical. It's where national laws are debated and passed, where policies are formulated, and where the executive branch is held accountable. It's the ultimate stage for the process of creation, production, and assembly of national governance, ensuring that the country has a guiding hand, in a way.
The Federal Structure: A Shared Responsibility
India follows a federal system of government. This means the country is divided into states and union territories, and each of these has its own government. The federal system is designed to allow for a shared responsibility between the central government and the state governments. It's a rather smart way to manage a country with so much diversity, actually.
This structure means that while there's a strong central authority, states also have significant autonomy to govern themselves on many issues. It's a balance of power, ensuring that local needs and cultural differences can be addressed while still maintaining national unity. This dual layer of governance is a key part of how the overall "making" of government operates in India, giving both national and regional voices a platform.
The federal system, in essence, allows for a more responsive and adaptable form of governance. It recognizes that what works in one part of India might not work in another, and so it empowers states to make their own decisions within a broader national framework. This collaborative approach is pretty central to the Indian way of doing things, you know.
Forming the Union Government: The Lok Sabha Elections
The primary way the Union Government, or Central Government, is "made" is through the Lok Sabha elections. These elections are a huge event, typically taking place across the country over several weeks. For example, the 2024 Lok Sabha elections were set to happen between April and May, which gives you a sense of the scale involved. It's a massive exercise in democratic participation, really.
During these elections, citizens aged 18 and above cast their votes for candidates in their respective constituencies. Each constituency elects one representative to the Lok Sabha. The party or group of parties that manages to secure more than half of the total seats in the Lok Sabha forms the government. This is known as achieving a majority, and it's absolutely crucial for forming a stable government, you see.
If no single party wins an outright majority, then different parties might come together to form a coalition government. This involves them agreeing to work together to reach the required number of seats. The whole process of these elections is the very act of the people constituting their government, choosing who will lead them at the national level, and that's pretty powerful.
The Role of Coalition Governments
Coalition governments have played a very significant role in India's political landscape, especially since the 1980s. When no single political party secures enough seats on its own to form a majority in the Lok Sabha, several parties join forces. This joining together is a common way the government gets "made" in such situations, allowing for a stable administration even without a single dominant party.
There are different views on these coalition governments. Some people believe that they tend to generate more inclusive policies, as various parties with different viewpoints have to compromise and work together. Others, however, feel that coalitions might impose constraints on policy making, making it harder to push through bold decisions. As Montek Singh Ahluwalia, a former deputy chairman of the Planning Commission, once noted, coalitions can certainly affect how policies are shaped, you know.
Despite these varying perspectives, coalitions are a practical reality in India's multi-party democracy. They represent a dynamic aspect of how the government is formed, showing a willingness among political groups to collaborate for the sake of governance. This adaptability in the "making" process is a key feature of India's political system, actually.
Accountability in the Process
A very important part of how government is "made" and how it functions in India is accountability. This refers to the process and the norms that ensure decision-makers are answerable to the people for whom decisions are taken. It's about ensuring that those in power are transparent about their actions and can be questioned by the public, which is rather fundamental to a healthy democracy.
Budget documents, for instance, are not just numbers; scrutinizing them allows one to understand the intention of the government, its priorities, policies, and how it allocates financial resources. This kind of scrutiny is a direct way to hold the government accountable for its "making" of policy and its use of public funds. It's a way for citizens to keep an eye on what their elected representatives are doing, you know.
The concept of accountability is woven throughout the entire fabric of Indian governance, from the local panchayats to the Parliament. It ensures that the "making" of government is not a one-time event, but an ongoing commitment to serving the public interest. This continuous process of being answerable is what keeps the system honest and responsive, in a way.
What the Government Does Once It Is Made
Once the government is "made" through elections and the formation of a majority, its work truly begins. This involves a lot of activities, from creating new tax rules, like the proposed changes in the income tax bill from 2026, to implementing major national initiatives. For example, the 'Make in India' initiative is a government effort to encourage companies to develop, manufacture, and assemble products within India, boosting local production. This is a very clear example of what a "made" government actually does, you know.
The government's priorities and policies are often revealed through its budget documents, which show how financial resources are allocated across different sectors. This planning and execution of policies are core to the government's function after its formation. It's about taking the ideas and promises from the election campaign and turning them into tangible actions for the country, which is quite a task.
Beyond policy-making, the government also provides various services to its citizens. The National Government Services Portal, for instance, aims to make online services from different government entities available on one platform. This shows how the "made" government works to facilitate access to public services, making things easier for people. It's all part of the ongoing process of governance, actually, after the initial formation.
Frequently Asked Questions About Government Formation
Here are some common questions people often have about how government is made in India:
Q: What are the main legislative bodies involved in making laws in India?
A: In India, there are mainly three legislative bodies that play a role in making laws and, by extension, forming government. At the very bottom, you have the local self-government, which could be a Gram Panchayat or a Municipality. Above them, there's the state legislative assembly in each state. And at the very top, you find the Parliament of India, which is the supreme legislative body, you know.
Q: How much majority is needed to form the government after Lok Sabha elections?
A: To form the government after Lok Sabha elections, a political party or a coalition of parties needs to secure a simple majority of seats. This means they need to win more than half of the total seats in the Lok Sabha. For instance, if there are 543 elected seats, a party or coalition would need to win at least 272 seats to form the government. It's a pretty straightforward rule, really.
Q: What is the difference between the Union Government and the Central Government?
A: The terms "Union Government" and "Central Government" are often used interchangeably, both officially and unofficially, to refer to the government of India. So, in essence, there isn't a practical difference in their meaning when people talk about the national government. They both point to the same entity that governs the entire country, which is rather convenient, you see.
Shaping the Future Together
The process of "making" government in India is a dynamic and continuous one, a true reflection of its democratic spirit. It's about the collective act of forming, causing, and bringing into being the leadership that guides the nation. From the foundational work of the Constitution to the grand scale of Lok Sabha elections and the everyday workings of local bodies, it’s a system designed to represent and serve its vast population, you know. Understanding this process gives us a deeper appreciation for how the country operates and how citizens play a part in shaping its destiny.
If you're curious to learn more about how different parts of the government work, you might want to learn more about on our site. There's so much to discover about the various roles and responsibilities that contribute to India's governance. You can also find more details by linking to this page to understand the finer points of legislative actions and public service initiatives. It’s a pretty rich topic, really.

History Of Making The Indian Constitution at Minnie Wilkin blog
Indian Government Structure Chart

Structure of the Government of India - YouTube