How Is India Politically Divided? Unpacking A Nation's Structure
You might be wondering, and it's a pretty big question, how exactly is India politically divided? This country, officially called the Republic of India, you know, it's a vast land in South Asia. It's a place that holds the greater part of that region, and it's a constitutional republic. This means, in a way, that its government gets its power from a set of rules, a constitution, and it looks after a truly varied population. We're talking about thousands of different groups of people living there, so that's quite a lot of diversity, isn't it?
India, to be honest, is geographically placed in both the northern and eastern parts of our planet. It's one of the oldest civilizations you'll find anywhere, with a really colorful mix of things and a deep, rich cultural past. This country, which is now, as a matter of fact, the most populous in the whole world, with about 1.4 billion people living there in 2024, has a political setup that's quite interesting to consider.
Understanding India's political layout means looking at its history, its government, and how its land is organized. It's not just about lines on a map; it's about how people live, how decisions get made, and how a truly massive country manages itself. So, let's just say, there's a good deal to talk about when we think about how India is set up politically.
Table of Contents
The Foundations of India's Political Map
Historical Splits and Unifications
The Republic's Government Structure
How India is Organized Today: States and Union Territories
The Role of Language and Identity in Divisions
Recent Changes to the Political Map
India's Place in South Asia's Political Landscape
The Foundations of India's Political Map
India, you see, is a country that really stands out in South Asia. It's a constitutional republic, and that's pretty important because it means the government's power comes from its written rules. This nation represents, in some respects, a truly diverse group of people, made up of thousands of different ethnic groups. It's a place that is geographically found in both the northern and eastern parts of the world, which is a bit unique.
The country, as a matter of fact, is one of the oldest civilizations around, and it has a truly rich cultural background, with a kaleidoscopic variety of traditions. This is a place, you know, that has seen so much history. It's also worth noting that India is now the most populous country on Earth, with an estimated 1.4 billion people living there in 2024, so that's a lot of folks.
The political layout of India, then, is shaped by its past, its current population, and its way of governing. It's a union of states and union territories, as stated in Article 1 of its constitution. This basic idea, you know, helps us understand how the country is put together and how its many different parts work together.
Historical Splits and Unifications
Looking back at India's political journey, especially from ancient times like the Mauryan period, you can see that India was, in a way, politically divided for many centuries. This division was often between Hindu and Muslim rulers. It was a time, you know, when different kingdoms held sway over different parts of the land, so there wasn't always one single authority.
This situation, you know, lasted until the British Crown took over and ruled the entire area. The British, in a sense, brought a different kind of political structure to the subcontinent. Then, in 1947, a really big event happened: the partition of British India. This was the division of the territory into two separate, independent states: the Union of India and the Dominion of Pakistan. The Union of India is, in fact, what we call the Republic of India today, and the Dominion of Pakistan became Pakistan.
The Dominion of India, then, had a rebirth on January 26, 1950. It became a sovereign democratic republic and a union of states. That day, you know, is celebrated every year as Republic Day, which is a national holiday. This historical background is pretty important for understanding how India's political map came to be, and how it's organized even now.
The Republic's Government Structure
The government of India, you know, is the political authority that looks after the Republic of India. It's set up with three main parts, or branches: the executive, the legislative, and the judicial. These branches, as a matter of fact, get their power directly from the Constitution of India. So, the constitution is like the big rulebook that tells everyone what they can and cannot do.
The executive branch, for instance, is responsible for carrying out the laws. The legislative branch, which is basically the parliament, is where laws are made and discussed. And the judicial branch, you know, handles legal matters and makes sure justice is served. This separation of powers is a pretty key feature of how the country runs, ensuring that no single part has too much control.
This structure, you know, helps keep things balanced and democratic. It's how the world's largest democracy operates, and it's quite a system to manage such a huge and diverse population. Each branch has its own job, but they all work together under the guidance of the constitution, which is, in a way, the supreme law of the land.
How India is Organized Today: States and Union Territories
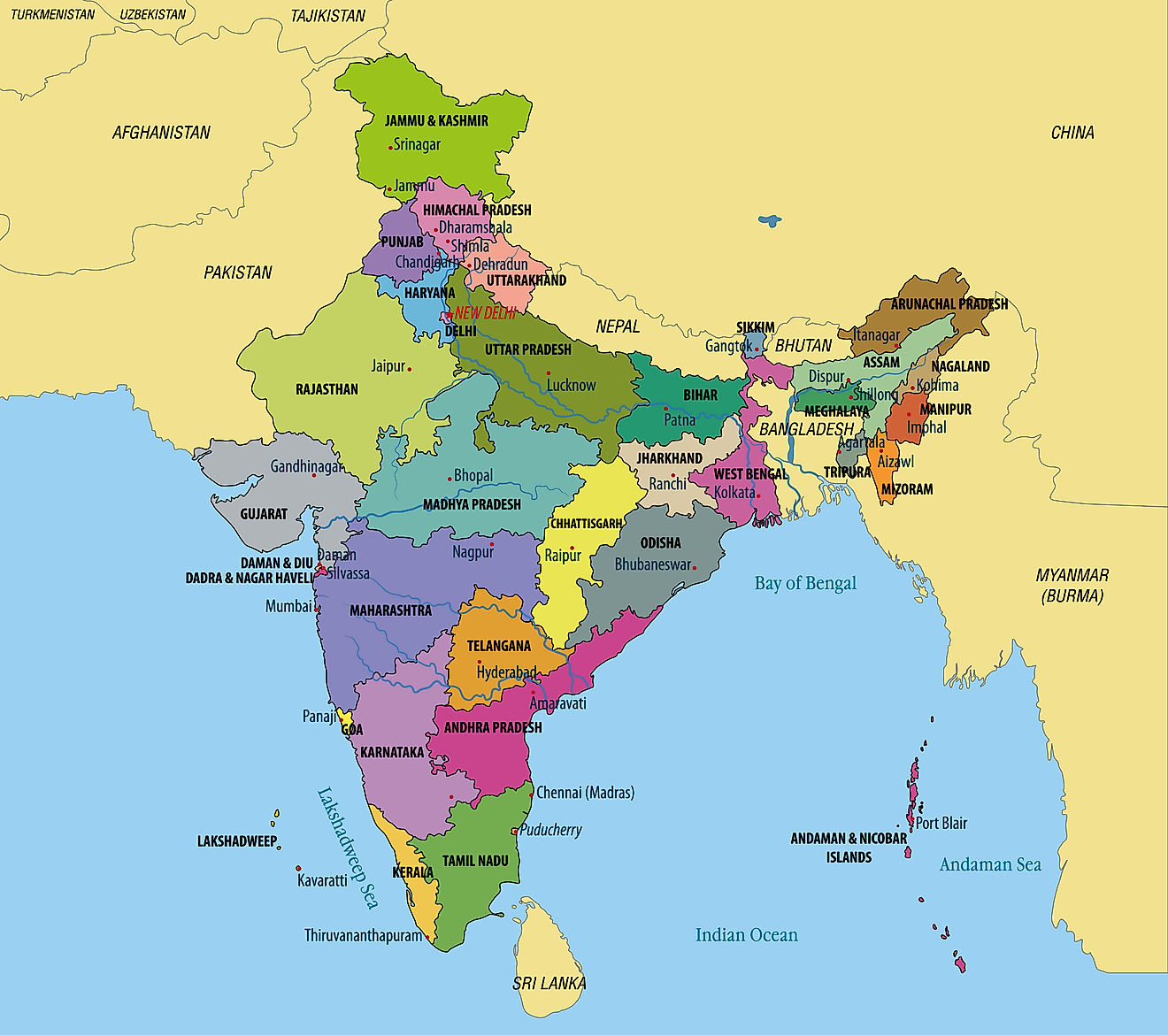
Politically, India is divided into 29 states and 7 union territories. This is how the country is set up, and it covers a very large area. The latest state to be formed was Telangana, which is a fairly recent addition to the map. This way of dividing the country into smaller, manageable parts is, you know, a very important part of its political system.
India was, as a matter of fact, divided into states and union territories according to the States Reorganisation Act of 1956. This act was pretty significant because it created states based on language and ethnicity. So, if people spoke the same language or shared a similar cultural background, they often ended up in the same state. This approach, you know, aimed to give different linguistic groups their own administrative areas.
These states, you know, are further broken down into smaller units called districts. Each state, in a way, has its own separate state government, which handles local matters. Some states and union territories are even further divided into what are called divisions, and these divisions are made up of groups of districts. This layered system, you know, helps in administering such a vast and populous nation, making sure that governance reaches every corner.
The Role of Language and Identity in Divisions
The way India's states were formed, you know, really shows how important language and identity are in the country's political divisions. The States Reorganisation Act of 1956 specifically created states based on shared languages and ethnic backgrounds. This meant that, for example, people who spoke Telugu largely ended up in one state, and those who spoke Marathi in another. This was, in a way, a very big step in how the country organized itself.
Before this, the system of how regions were divided was quite different. But after 1956, the idea was that people who had a common language would feel more connected to their state government and administration. This approach, you know, aimed to reduce potential conflicts and make governance more effective by respecting the linguistic diversity of the population. It's a pretty unique way to draw political lines, if you think about it.
This method of division, you know, helped give a voice to different cultural groups and allowed them to preserve their distinct heritage. It's a system that, in some respects, reflects the kaleidoscopic variety of India itself, where many different ways of life and languages coexist. So, the political map is not just about geography; it's very much about the people and their shared identities.
Recent Changes to the Political Map
The political map of India, you know, isn't something that stays completely still. There have been some recent changes, for instance, that are worth noting. One big one involves the erstwhile state of Jammu and Kashmir. This state was, as a matter of fact, bifurcated, or split, into two union territories: Jammu and Kashmir, and Ladakh. This happened as per the Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation Act of 2019, on the 5th of August.
This change, you know, meant a significant shift in the administrative structure of that region. It's a demonstration that the country's political divisions can, in a way, be updated and changed over time. While the text mentions 29 states and 7 union territories, this specific event of the J&K reorganization means that the number of states and union territories can shift, so it's a dynamic situation.
These kinds of updates to the map, you know, show that the government of India is always looking at how best to administer its vast land and diverse people. It's a process that, you know, involves political decisions and legal changes to reshape how the country's parts are managed. Learn more about how governance works on our site, and you can also find out more about India's administrative history here.
India's Place in South Asia's Political Landscape
South Asia, the region where India is located, is, you know, politically divided into nine independent countries. These include Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, India itself, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Bhutan, Nepal, Iran, and the Maldives. This whole region, as a matter of fact, covers a very large area, roughly 3,218,688 square kilometers, and it has a huge population.
India, being the largest country in this group and the most populous in the world, plays a pretty central role in the region. It shares borders with Pakistan to its northwest, and that's a pretty significant border, you know. The way India is politically structured, with its states and union territories, also influences how it interacts with its neighbors.
The political situation in India, you know, often has an effect on the wider South Asian region. As India heads to the polls, for instance, in what will be the biggest democratic election the world has ever seen, questions about what democracy means in India become even more important. The country's political divisions and how it manages them are, in a way, a key part of its identity on the world stage, and it's something that really shapes its relationships with other nations. You can find more information about the political makeup of countries in South Asia on reputable government portals, like this one: India.gov.in.
Frequently Asked Questions About India's Political Divisions
How many states and union territories does India have?
India is politically divided into 29 states and 7 union territories, according to our source text. However, you know, there have been some recent changes, like the bifurcation of Jammu and Kashmir into two union territories, which can shift the exact count of these administrative units.
What was the basis for dividing states in India?
The states in India were, in a way, created based on language and ethnicity. This happened as per the States Reorganisation Act of 1956. This means that groups of people who spoke the same language or shared similar cultural backgrounds often formed their own states, which is a pretty interesting way to organize a country.
When did India become a sovereign democratic republic?
The Dominion of India was, you know, reborn as a sovereign democratic republic and a union of states on January 26, 1950. That day is, as a matter of fact, celebrated every year as Republic Day, which is a big national holiday in the country.

India Political Map Hd

Partition of India Mapped - Vivid Maps
India Maps & Facts - World Atlas